Channels¶
Linear channel¶
-
class
tramp.channels.LinearChannel(W, precompute_svd=True, name='W')[source]¶ Linear channel x = W z.
- Parameters
W (-) –
precompute_svd (-) – if True precompute SVD of W = U S V.T
name (-) – name of weight matrix W for display
-
class
tramp.channels.ComplexLinearChannel(W, precompute_svd=True, name='W')[source]¶ Complex linear channel x = W z.
- Parameters
W (-) –
precompute_svd (-) – if True precompute SVD of W = U S V.conj().T
name (-) – name of weight matrix W for display
Notes
For message passing it is more convenient to represent a complex array x as a real array X where X[0] = x.real and X[1] = x.imag
In particular: - input of sample(): Z array of shape (2, z.shape) - output of sample(): X array of shape (2, x.shape) - message bz, posterior rz: real arrays of shape (2, z.shape) - message bx, posterior rx: real arrays of shape (2, x.shape)
-
class
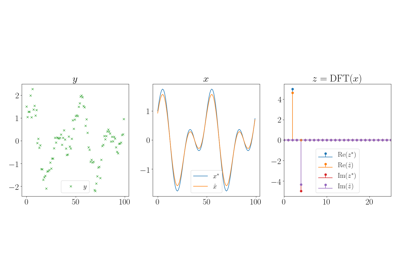
tramp.channels.DFTChannel(real=True)[source]¶ Discrete fourier transform x = FFT z.
- Parameters
real (-) – If z supposed to be real
Notes
The fft and ifft are scaled by sqrt(N) so that both are unitary.
For message passing it is more convenient to represent a complex array x as a real array X where X[0] = x.real and X[1] = x.imag
In particular: - output of sample(): X array of shape (2, x.shape) - message bx, posterior rx: real arrays of shape (2, x.shape)
- And if real=False (z complex):
input of sample(): Z array of shape (2, z.shape)
message bz, posterior rz: real arrays of shape (2, z.shape)
Examples using tramp.channels.DFTChannel¶
-
class
tramp.channels.ConvChannel(filter, real=True)[source]¶ Conv (complex or real) channel x = w * z.
- Parameters
filter (-) – Filter weights. The conv weights w are given by w[u] = f*[-u]. The conv and filter weights ffts are conjugate.
real (-) – if True assume x, w, z real if False assume x, w, z complex
Notes
For message passing it is more convenient to represent a complex array x as a real array X where X[0] = x.real and X[1] = x.imag
In particular when real=False (x, w, z complex): - input of sample(): Z real array of shape (2, z.shape) - output of sample(): X real array of shape (2, x.shape) - message bz, posterior rz: real arrays of shape (2, z.shape) - message bx, posterior rx: real arrays of shape (2, x.shape)
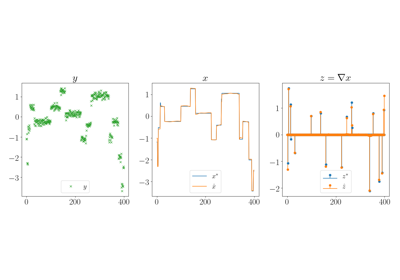
Examples using tramp.channels.GradientChannel¶
-
class
tramp.channels.UnitaryChannel(U, name='U')[source]¶ Unitary channel x = U z.
- Parameters
U (-) –
name (-) – name of unitary matrix U for display
Notes
For message passing it is more convenient to represent a complex array x as a real array X where X[0] = x.real and X[1] = x.imag
In particular: - input of sample(): Z array of shape (2, z.shape) - output of sample(): X array of shape (2, x.shape) - message bz, posterior rz: real arrays of shape (2, z.shape) - message bx, posterior rx: real arrays of shape (2, x.shape)
Piecewise linear activation¶
Others¶
-
class
tramp.channels.ModulusChannel[source]¶ Modulus channel \(x = |z|\).
Notes
For message passing it is more convenient to represent a complex array x as a real array X where X[0] = x.real and X[1] = x.imag
In particular: - input of sample(): Z array of shape (2, z.shape) - message bz, posterior rz: real arrays of shape (2, z.shape)