Note
Click here to download the full example code
Compressed Sensing¶
import pandas as pd
from tramp.models import glm_generative
from tramp.experiments import BayesOptimalScenario, qplot, plot_compare
from matplotlib import rcParams
rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
Model¶
We wish to infer the sparse signal \(x \sim \mathcal{N}_{\rho}(.) \in \mathbb{R}^N\) from \(y \sim \mathcal{N}(Fx, \Delta) \in \mathbb{R}^M\), where \(F \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N}\) is a Gaussian random matrix.
teacher = glm_generative(
N=1000, alpha=0.8, ensemble_type="gaussian", prior_type="gauss_bernoulli",
output_type="gaussian", output_var=1e-11, prior_rho=0.5
)
scenario = BayesOptimalScenario(teacher, x_ids=["x"])
scenario.setup(seed=42)
scenario.student.plot()
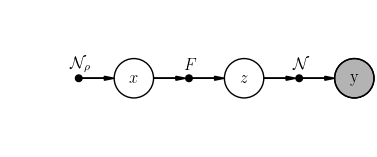
EP dynamics
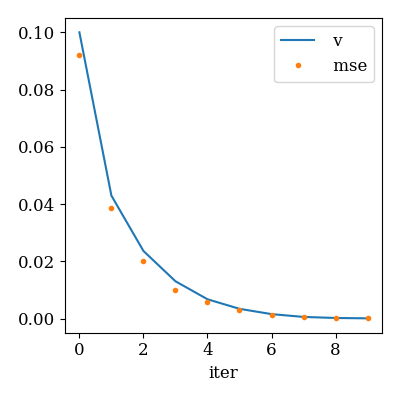
ep_evo = scenario.ep_convergence(metrics=["mse"], max_iter=10)
qplot(
ep_evo, x="iter", y=["v", "mse"], y_markers=["-", "."],
y_legend=True
)
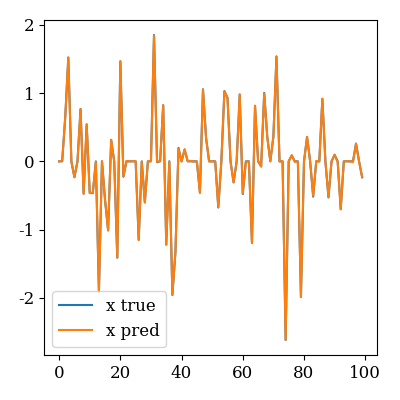
Recovered signal
plot_compare(scenario.x_true["x"], scenario.x_pred["x"])
Compare EP vs SE¶
See data/compressed_sensing_ep_vs_se.csv.py for the corresponding script.
rename = {
"alpha": r"$\alpha$", "prior_rho": r"$\rho$",
"source=": "", "n_iter": "iterations"
}
ep_vs_se = pd.read_csv("data/compressed_sensing_ep_vs_se.csv")
qplot(
ep_vs_se, x="alpha", y="v", marker="source", column="prior_rho",
rename=rename, usetex=True, font_size=16
)
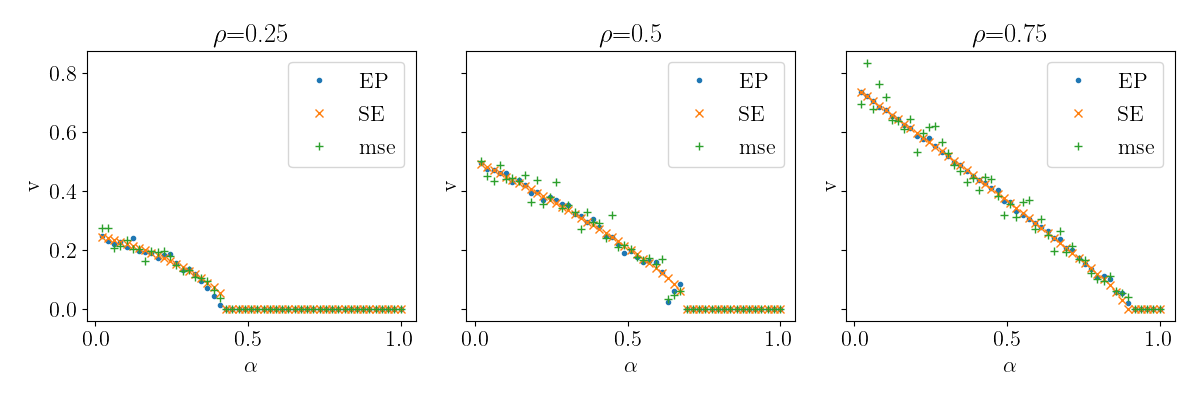
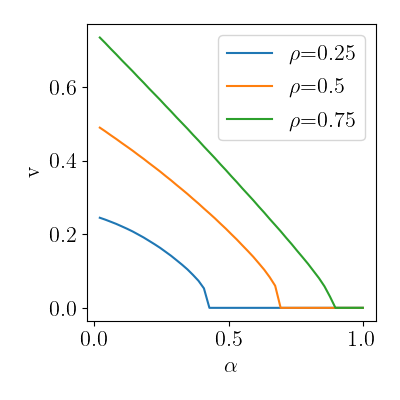
Phase transition
qplot(
ep_vs_se.query("source=='SE'"),
x="alpha", y="v", color="prior_rho",
rename=rename, usetex=True, font_size=16
)
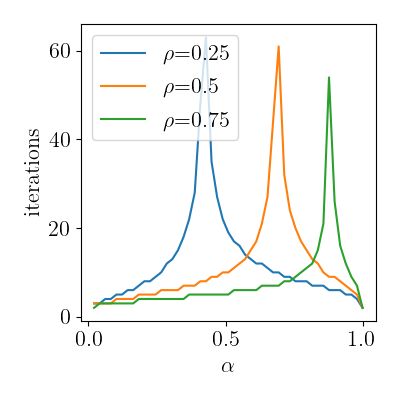
Number of iterations diverging at the critical value
qplot(
ep_vs_se.query("source=='SE'"),
x="alpha", y="n_iter", color="prior_rho",
rename=rename, usetex=True, font_size=16
)
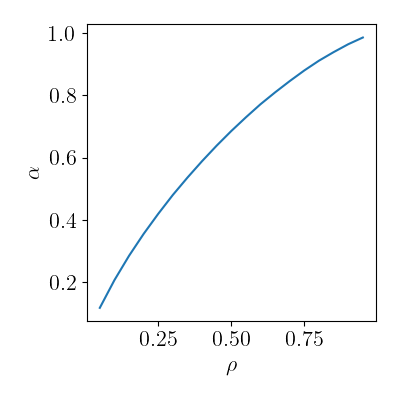
Critical lines.
crit = pd.read_csv("data/cs_critical_lines.csv")
qplot(
crit,
x="prior_rho", y="alpha",
rename=rename, usetex=True, font_size=16
)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 3.604 seconds)